General setup
We will focus on distributed meshes as they are often used in parallelized finite element codes, such as FEniCS or deal.II. In a distributed memory parallelization, the ranks usually only own a fraction of the mesh. At the interface between two partitions of the mesh vertices or elements owned by one rank usually have to be communicated to another one in order to make sure that all the information needed for the computations is available.
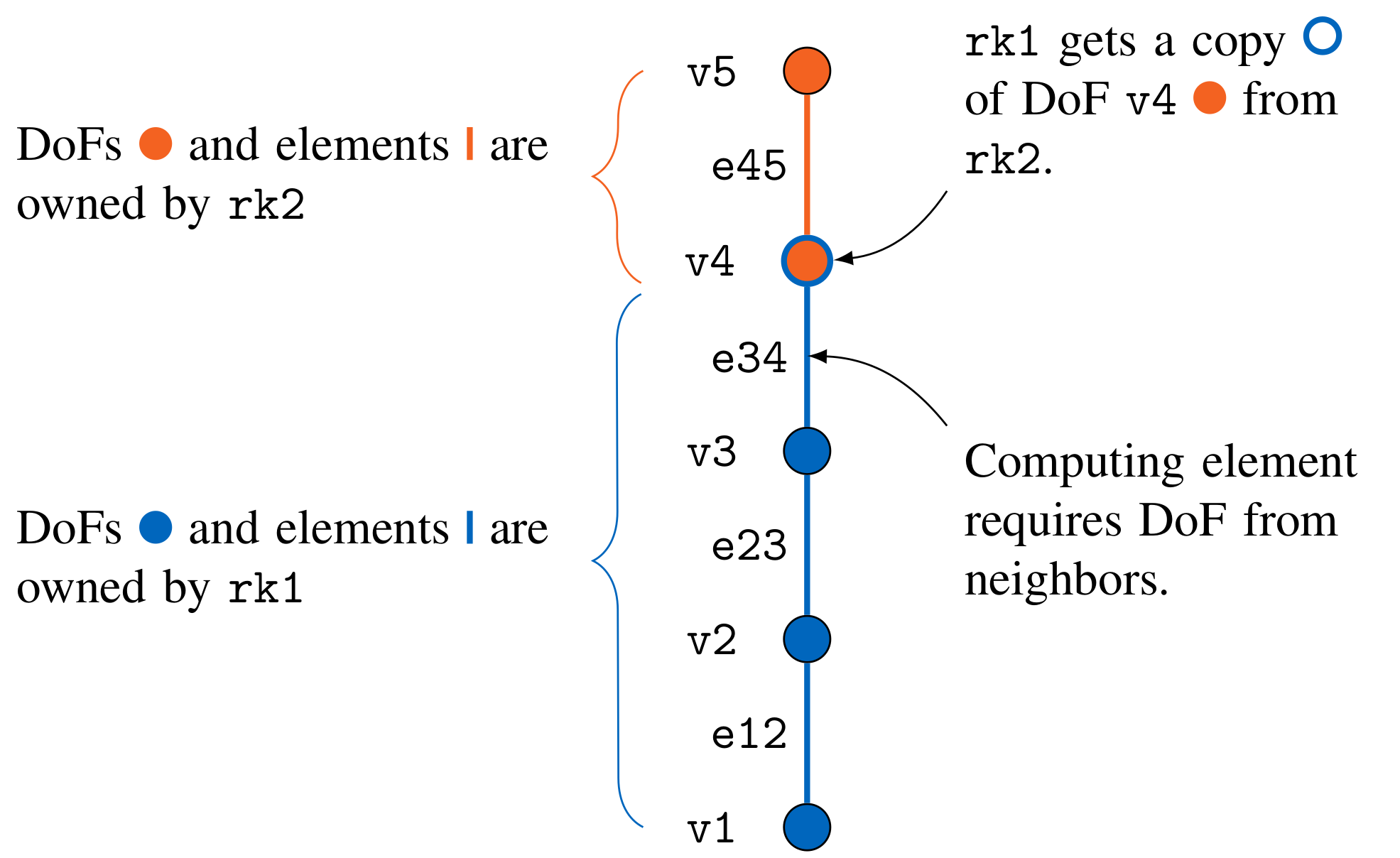
This distributed mesh setup is not only relevant for the internal degrees of freedom, but also for the coupling mesh of preCICE: The ranks have to call precice::setMeshVertex(...) or precice::setMeshVertices(...) to define the coupling mesh. In the following we want to discuss strategies how preCICE can be used in such a situation and how we can deal with the need for duplicate vertices.
Use a single mesh and communicate values for copied vertices inside adapter
In this approach we do not define any copied vertices in preCICE, but only the vertices owned by a rank. Therefore, each vertex is globally only defined once via precice::setMeshVertex(...). The rank that owns the vertices uses the read and write functions of preCICE (precice::readData(...) and precice::writeData(...)) to update the coupling data on the mesh.
Note that it might be required to add another communication step inside the adapter or the solver to synchronize the data on the copied vertices among ranks.
Discussion of this approach:
- Only one mesh is needed.
- Same
precice-config.xmlas for serial case. - Additional communication step after preCICE communication is complete might be required.
- Mesh connectivity information is restricted to vertices owned by the rank. Therefore
precice::setMeshEdge(...)cannot be called for edges that cross the border between two ranks.
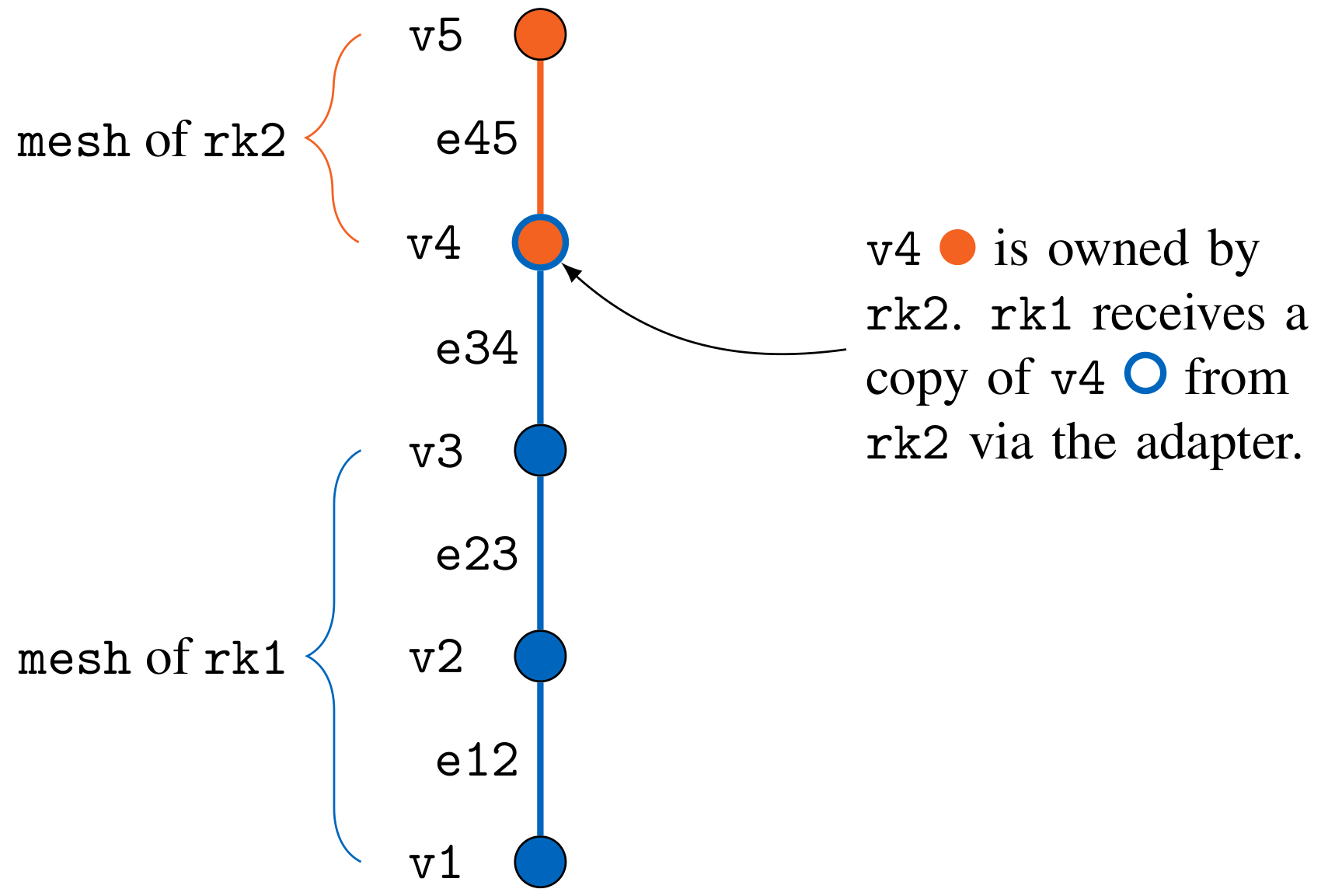
Use a single mesh and duplicate copied vertices
Each rank can only access the vertices that it has previously defined. Therefore, in this approach we have to call precice::setMeshVertex(...) for all vertices owned by the rank and for vertices where the rank requires access to a copy, since we will have to read coupling data from these vertices, as well. Note that we will additionally have to write data to copied vertices, since they are equal to owned vertices from the perspective of preCICE.
Since we have to write duplicate vertices, it becomes especially important to make sure that the values written by the rank that owns the vertices and the rank(s) where the vertices are only a copy of the original vertex are written correctly: If a conservative mapping is used, only a single rank (usually the rank that owns the vertex) is allowed to write the updated values to preCICE, since otherwise the mapping of preCICE will cause the actual value to be a multiple of the “true” result. If a consistent mapping is used, all ranks that define the vertex also have to write the “true” value to it, since otherwise the result will be a combination of the “true” value and zeroes originating from the ranks owning copies of the vertex.
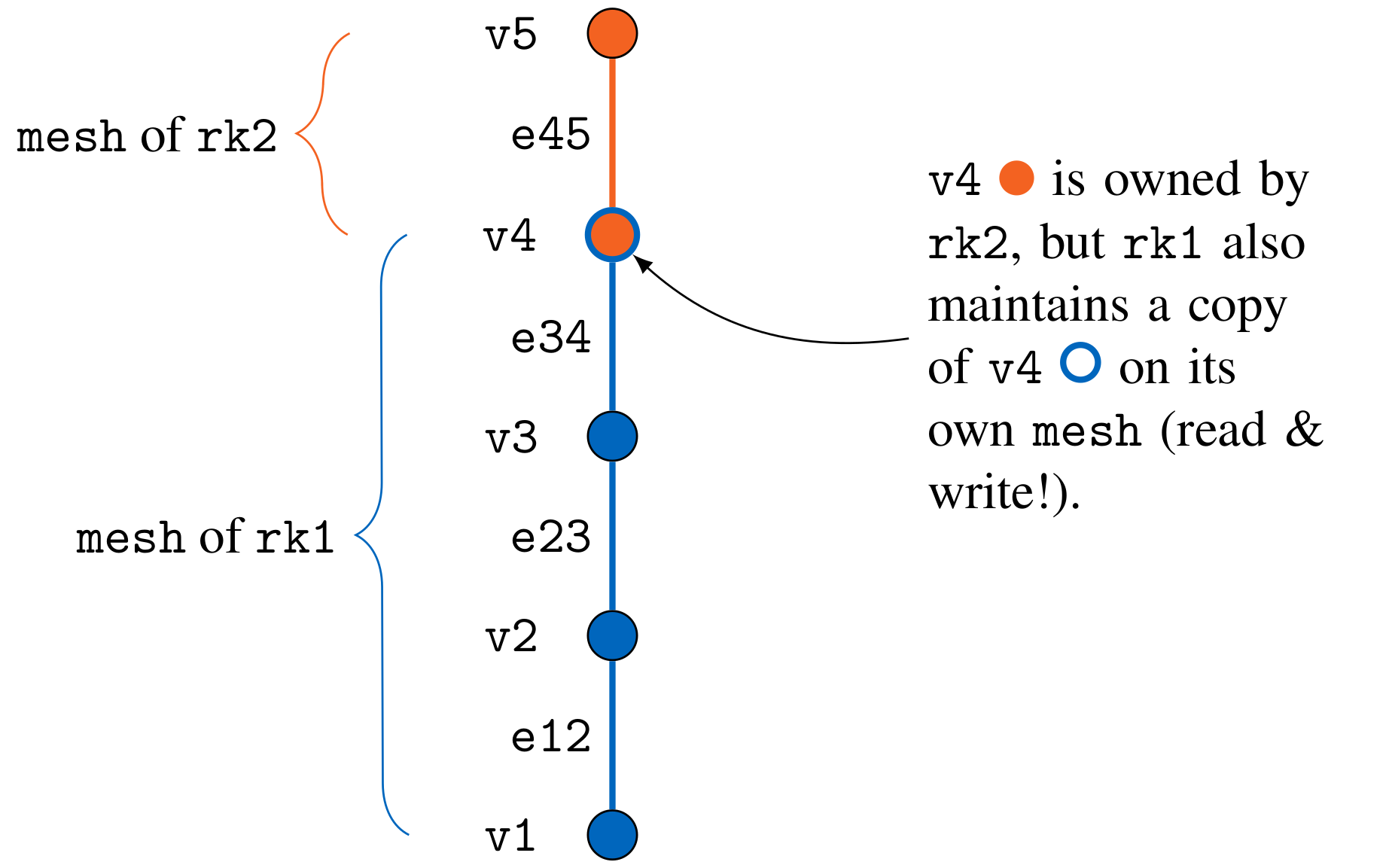
Discussion of this approach:
- Only one mesh is needed.
- Same
precice-config.xmlas for serial case can be used. - User must call write function for owned and copied vertices correctly depending on the mapping technique used to avoid mistakes.
- Mesh connectivity information is available for vertices owned by the rank and the direct neighborhood. The adapter can
precice::setMeshEdge(...)for edges that cross the border between two ranks.
Define two separate meshes as read_mesh and write_mesh
We create a write_mesh where we call precice::setMeshVertex(...) only for the vertices owned by the rank. We do no add any copies of vertices to the write_mesh, since they are owned by another rank and only the rank having ownership is allowed to write values (e.g. via precice::writeData(...)) to vertices on that mesh.
Additionally, we create a read_mesh, where we call precice::setMeshVertex(...) for vertices owned by the rank and vertices where a copy is required. This allows the rank to read the values for owned as well as for copied vertices (e.g. via precice::readData(...)).
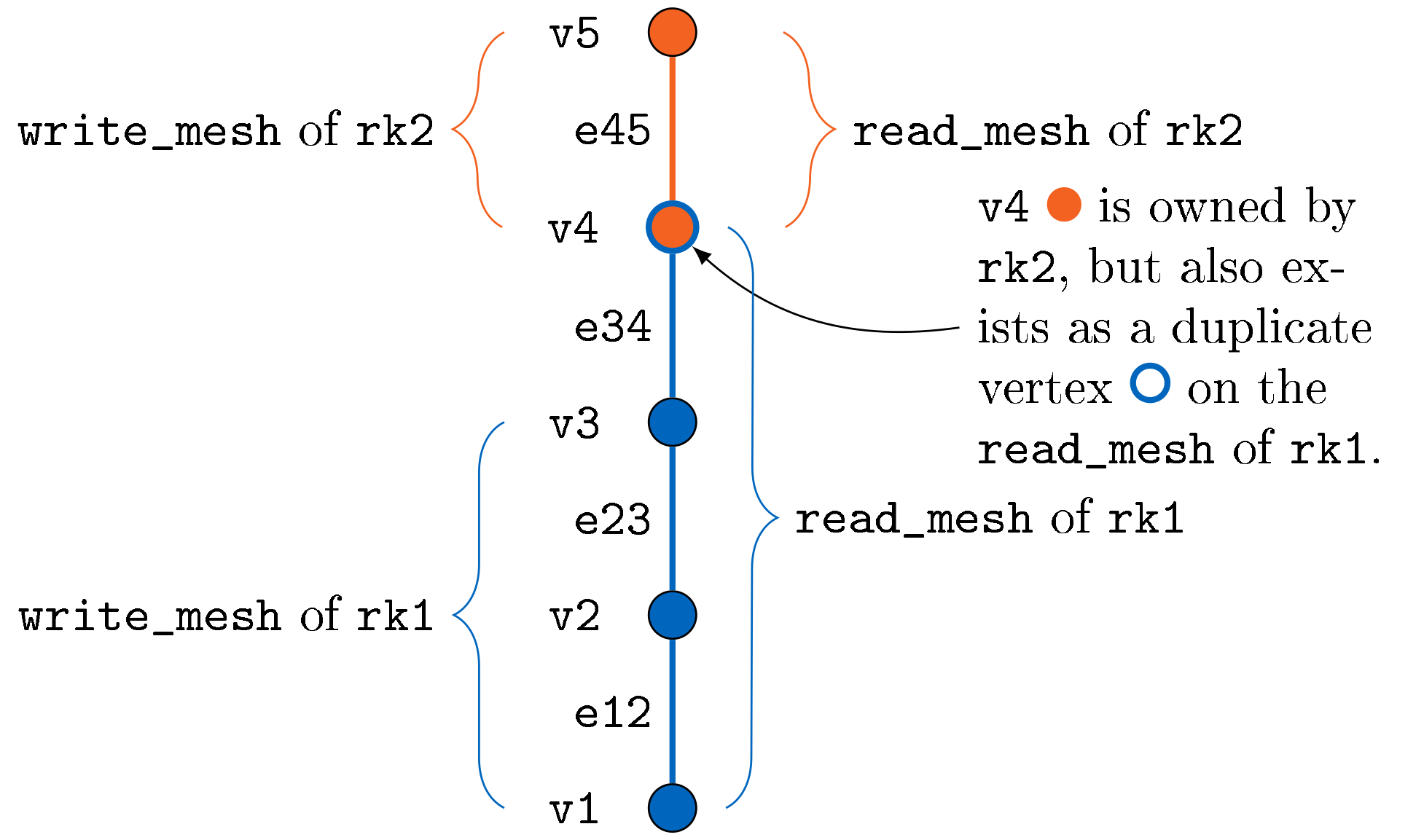
Discussion of this approach:
- User has to deal with two meshes.
precice-config.xmlbecomes more complex than for the serial case.- The mapping of preCICE is taking care of providing information for copied vertices to ranks that would otherwise not be able to access these vertices.
- Mesh connectivity information is restricted to vertices owned by the rank. Therefore
precice::setMeshEdge(...)cannot be called for edges that cross the border between two ranks.